Max McBride provides quantitative results of his aversion therapy experiments.
- Type
- Academic / Technical Report
- Source
- Brigham Young University LDS
- Hearsay
- Direct
- Reference
Max McBride, "Effect of visual stimuli in electric aversion therapy," PhD Dissertation, Brigham Young University, Department of Psychology, 1976
- Scribe/Publisher
- Brigham Young University
- Audience
- Reading Public
- Transcription
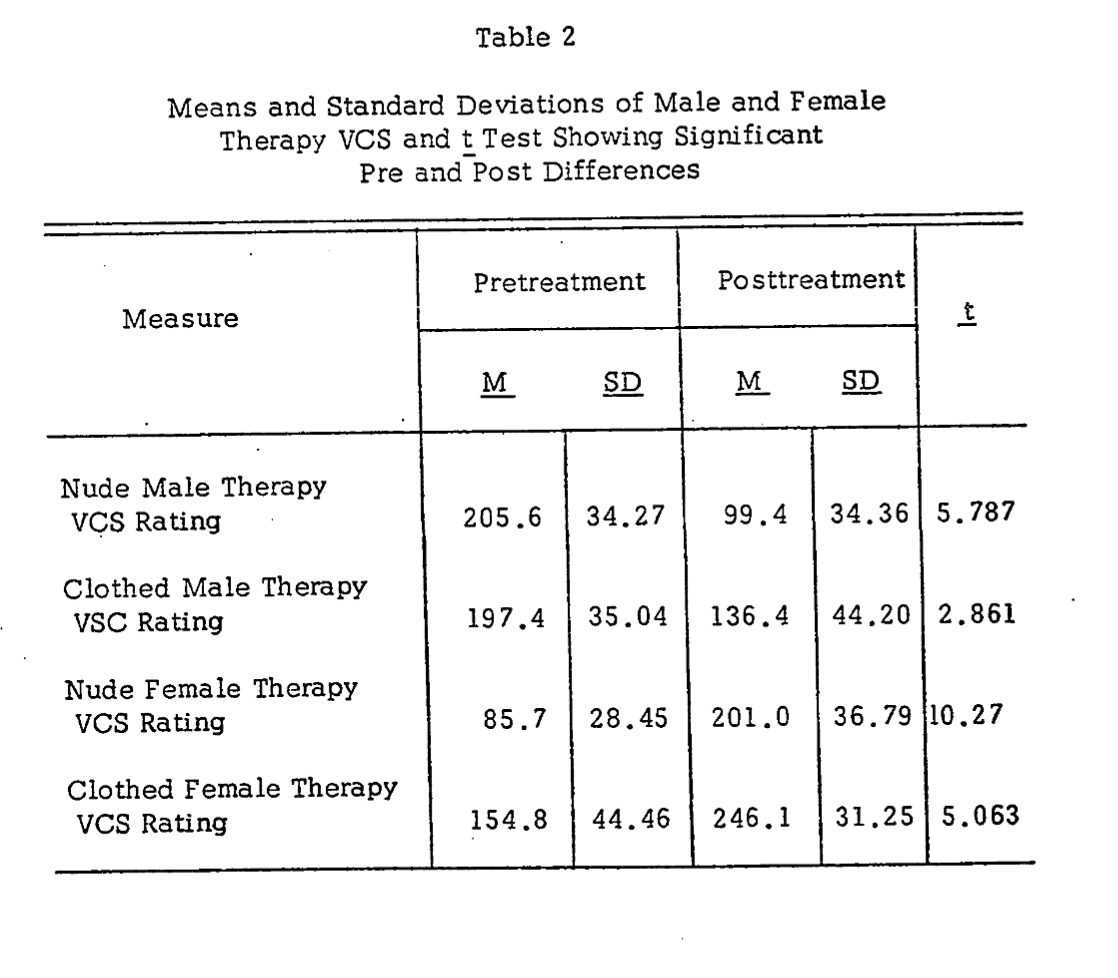
Posttreatment evaluation of male therapy VCS showed that N-group rated their slides significantly less attractive than did C-group, (t= 1.748, p <,10). See Table 1, The posttreatment measures were 99.4 for N-group and 136.4 for C-group suggesting that ratings of male therapy VCS had decreased more for Ss using nude slides (VCS) of males than for Ss using clothed slides (VCS) of males.
Even though posttreatment differences were significant between groups the decline in rating of the male therapy VCS was significant for both groups which suggests that aversive treatment effectively decreased ratings to nude and clothed male VCS. As seen in Table 2, this is substantiated by the significant pre and post differences for both the N-group. (t=5.787, 5 < .001) and C-group (t=2.861, 5 < .05).
. . .
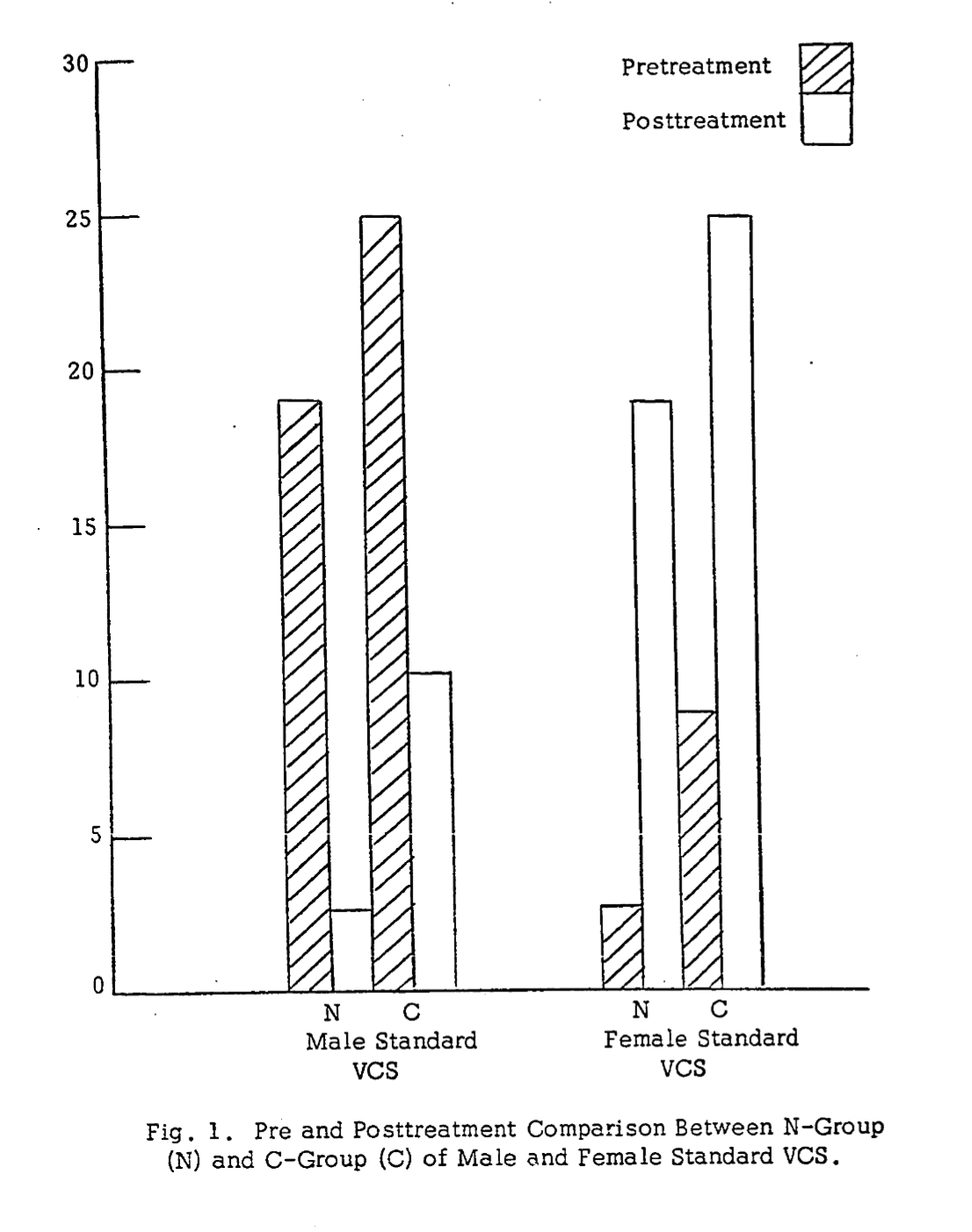
In comparing (see Figure 1) the pre and posttreatment scores for the male and female standard VCS across both treatment groups, pretreatment penile erection to these stimuli were reversed, Pretreatment penile erection averaged 22/mm to male standard VCSs and 5.2/mm to female standard VCS. Posttreatment penile erection averaged 6.6/mm to male standard VCS and averaged 22.2/mm to female standard VCS. A reading of 25/mm represented a full erection.
. . .
Sexual Orientation, Before and After Treatment
No significant differences were manifest between treatment groups in pretreatment evaluation of current sexual orientation. This finding shows that both groups evaluated themselves at the same level of homosexual orientation, Differences between the two mean scores was 1.2; N-group's mean score was 66.1, and C-group's mean score was 67.3. Neither was there a significant difference between groups in their posttreatment sexual orientation evaluation, However, both groups subjectively evaluated themselves as more heterosexual than homosexual at the conclusion of treatment, Posttreatment improvement of subjective evaluations of sexual functioning supported the improved posttreatment therapy VCS ratings and standard VCS pleythysmographic measures: That is, all measures showed significant positive therapeutic effect.
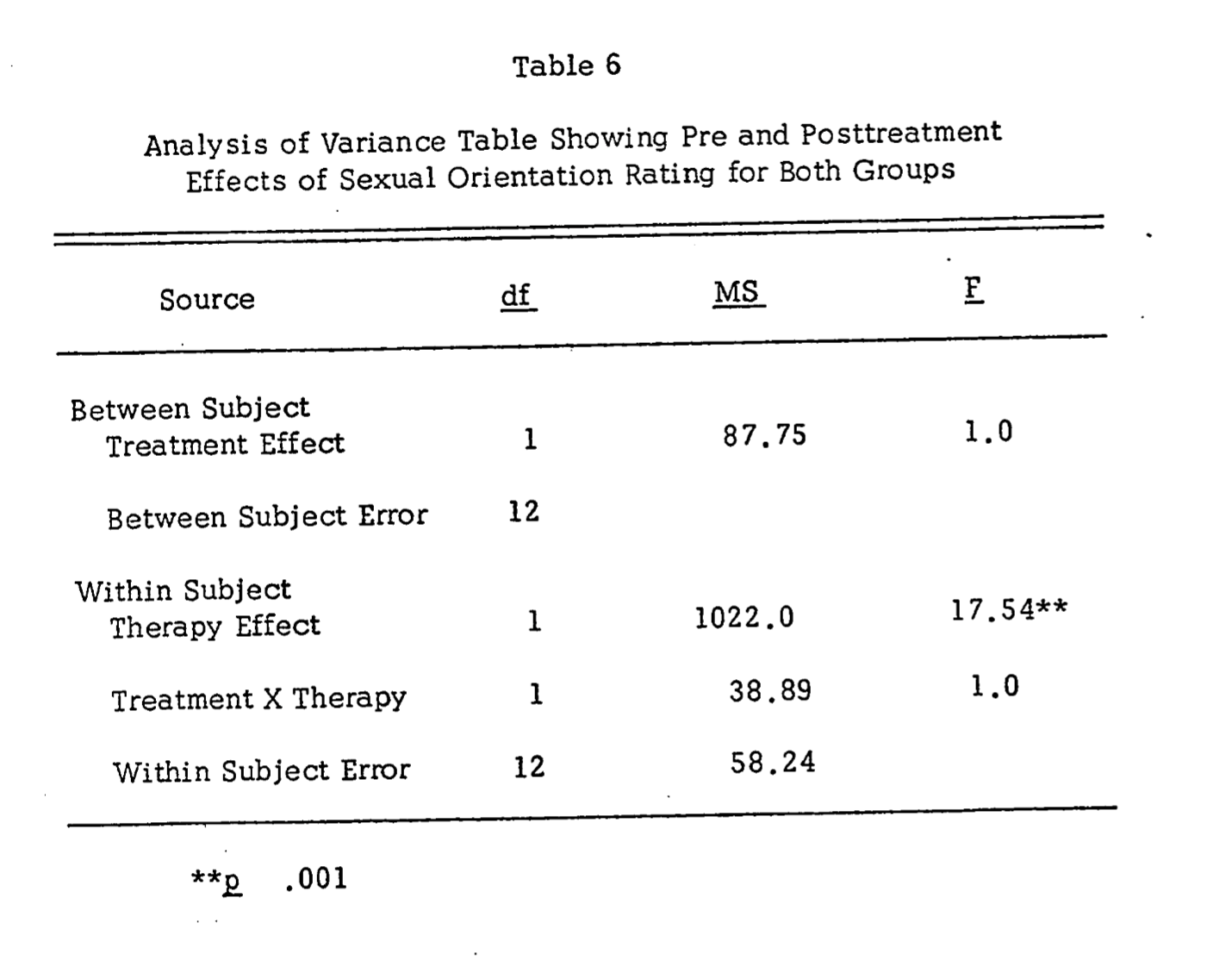
Analysis of differences between groups on the sexual orientation measure indicated a highly significant therapy effect only (F = 17.54, p <.001), showing that at the conclusion of treatment, both treatment groups evaluated themselves as significantly less homosexual than heterosexual (see Table 6). This finding suggests that the type of Behavior Therapy used in the present study was highly effective in changing subjective evaluation of sexual orientation, as measured two weeks subsequent to treatment termination.
- Citations in Mormonr Qnas
The B. H. Roberts Foundation is not owned by, operated by, or affiliated with the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.