The Temple Endowment and Freemasonry
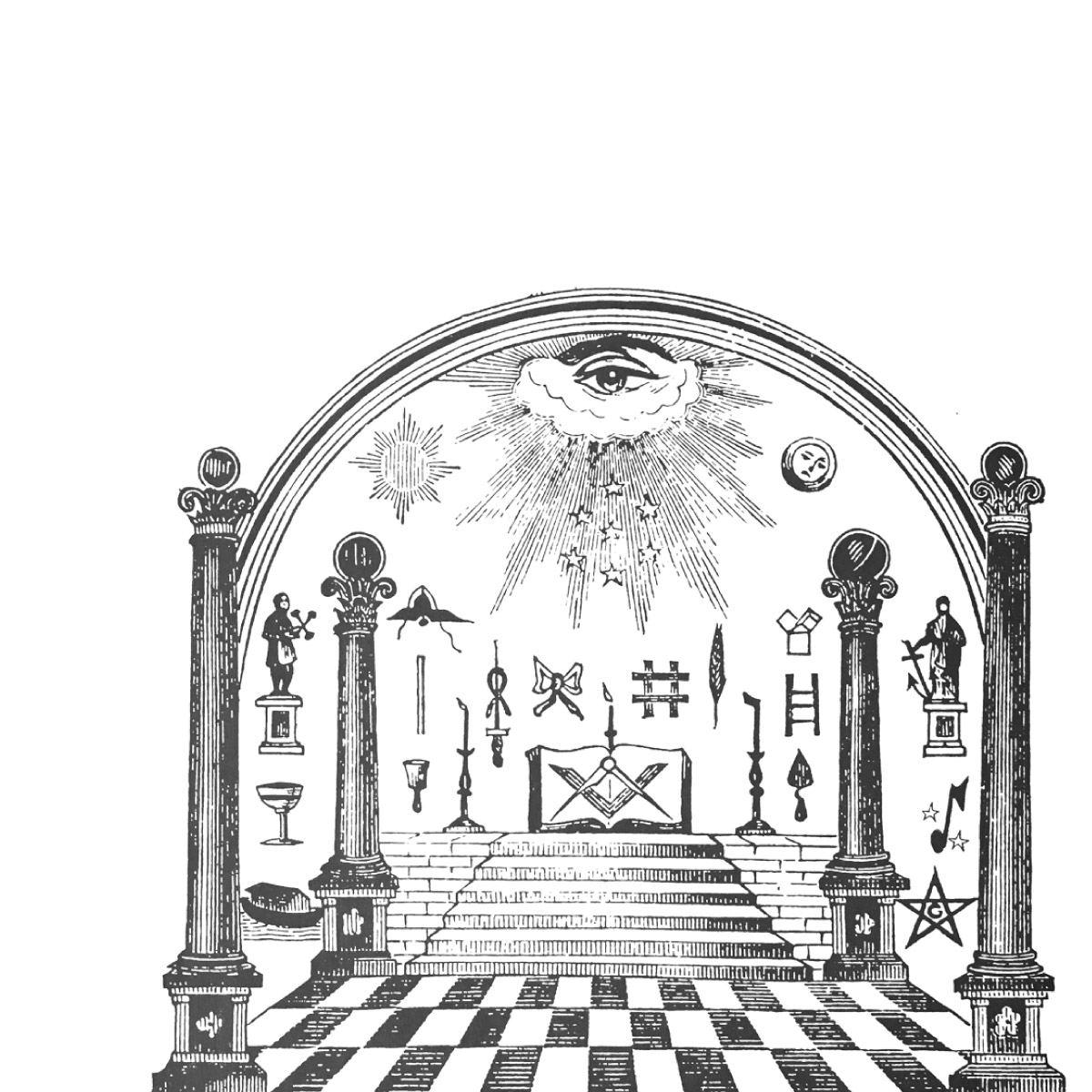
Freemasonry, the Temple Endowment, and Early Latter-day Saints
1300s
Christian stonemasons form professional brotherhoods or guilds in England.[1]
~400 years pass
June 24, 1717
The Grand Lodge of England is established and allows membership for people who are interested in Masonic ideas but who are not stonemasons.[2]
~100 years pass
September 1826
May 15, 1829
April 6, 1830
Joseph Smith organizes the Church of Christ, later renamed The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.[7]
March 15, 1831
July 1832–July 1833
September 22–23, 1832
October–November 1835
January 21, 1836
April 3, 1836
June 27–July 2, 1839
November 1839
April 6, 1840
The Illinois Grand Lodge is reorganized on the tenth anniversary of the organization of the Church, and Judge James Adams is elected Deputy Grand Master.[30]
January 19, 1841
June 23, 1841
October 15, 1841
December 29–30, 1841
January 6, 1842
In his journal, Brigham Young records the events of the day in a Masonic code that reads: "I was taken into the lodge," which may indicate that he had been initiated before the Nauvoo Lodge had been formally installed, which would have been a serious breach of Masonic regulations.[38]
March 15, 1842
March 15, 1842
March 16, 1842
Joseph and Sidney are passed as second-degree (Fellow Craft) Masons and raised as third-degree Master Masons of Ancient York Masonry, sign the by-laws of the Lodge, and become full members.[42]
March 17, 1842
March 20, 1842
Joseph teaches about "certain key words and signs" that are necessary "for man to receive a celestial glory."[45]
May 1, 1842
Joseph Smith delivers a sermon outlining the importance of the "keys" and "signs" that the Saints would soon be given in the temple.[46]
May 4, 1842
Joseph introduces the endowment ordinance to a group of nine Latter-day Saint Freemasons.[47]
May 4, 1842
Abraham Jonas writes a letter to the Nauvoo Lodge warning that the Nauvoo Freemasons are "regarded by some, with some mistrust" and that John C. Bennett was an expelled Mason and a "very bad man."[48]
May, 1842
June 17, 1842
July 8, 1842
August 6, 1842
James Adams joins Joseph Smith and others in a visit to Montrose, Iowa, to install a new lodge.[55]
August 11, 1842
Nauvoo Freemasons learn that Grand Master Abraham Jonas placed an injunction against the Nauvoo Lodge for alleged "irregularities" until an investigation could be made.[56] The injunction was in response to concerns about Bennett's character and allegations and additional issues raised by the Bodley Lodge No. 1 at Quincy.[57]
October 1842
November 2, 1842
October 4, 1843
Late 1842
John C. Bennett publishes an exposé of the Church and its temple rites.[65]
November 1843
Hyrum Smith addresses the Nauvoo Lodge, condemning what he saw as the "ungenerous" and "unmasonic" treatment they had received from the Illinois Grand Lodge.[66]
April 5, 1844
The Nauvoo Masonic Temple is dedicated by Hyrum Smith.[67]
June 27, 1844
Joseph and Hyrum Smith are killed in Carthage. Joseph reportedly invokes a formal Masonic sign of distress that may have been directed to Freemasons in the mob.[68]
October 1844
The Grand Lodge definitively withdraws fellowship from the Latter-day Saint Lodges.[69]
February 1846
Nauvoo Lodge meetings continue even after the first group of Saints begins the trek West.[70]
What is Freemasonry?
Freemasonry[71] is a fraternal group that was formally organized in the 1700s based on the symbols and practices of medieval stonemasons who were free to travel for work.[72][73] Today, the organization is still members-only and focuses on personal development through brotherhood, charity, and truth.[74]
While not a religion,[75] it draws from sources like the Bible,[76] Christianity,[77] other ancient sources,[78] and Enlightenment philosophy.[79]
Is Freemasonry connected to devil worship or some type of world government?
At times, Freemasonry has been rumored to be connected with devil worship[80] or conspiring to take over the world,[81] but these ideas have been debunked.[82]
Does Freemasonry date back to ancient times?
No, probably not. Historians debate the origins of Freemasonry's symbols and rituals, but most agree they don’t come directly from ancient times.[83] Freemasonry mentions ancient traditions such as the building of Solomon’s Temple,[84] but these are seen more as stories and symbols than actual history.[85]
What is the connection between Freemasonry and the Church?
Joseph Smith[BIO] became a Freemason in March 1842.[86][87] Soon after, he introduced the temple endowment to the Saints,[88] which shares some elements with Masonic rituals.[89]
Why did Joseph Smith become a Freemason?
It's unclear. There are no historical sources explaining why Joseph became a Freemason.[90] This decision could be related to Hyrum Smith (and possibly Joseph Smith Sr.)[91] becoming a Freemason or another reason entirely.
Some historians have speculated that Joseph may have been attracted to the believed ancient origins of Freemasonry or their shared values,[92][93] or also that he may have been interested in preparing for temple ordinances or building community and support.[94][95]
Does the temple ceremony come from Masonic rituals?
Yes, at least some parts of it.[96] Other elements of the temple ceremony can also be found in the Old Testament[97] and the Book of Abraham.[98]
So did Joseph Smith copy the Masonic rituals?
Probably parts of it. Some early Latter-day Saints commented on the similarity between the temple endowment and Freemason rituals.[99]
What are the main similarities between Freemasonry and the Nauvoo temple ordinances?
There are some specific ritual gestures (such as certain handclasps) and ritual patterns (such as repetition, lectures, and questions and answers) that share similarities.[100]
What are the main differences between the two?
There are many elements in the endowment that are not found in Freemasonry and vice versa. For example, the endowment contains washings and anointings and depictions of the Creation and the Fall of Adam and Eve, which are all absent from Craft Freemasonry that Joseph Smith was familiar with.[101]
Furthermore, the endowment does not include ceremonial tools like the rough ashlar and trestle board, and symbols like the letter "G" or the beehive, which are prominent in Masonry.[102]
There are also differences in the overall function and purpose between the two. For example, unlike in the endowment ceremony, participants in Masonic rituals do not make covenants with God, but rather take obligations upon themselves, with the members of the Lodge and with God as witnesses.[103][104]
I've heard about "penalties" in the temple endowment. Were penalties part of the Freemason rituals?
Yes. Masonic ceremonies reportedly contained promises to not reveal any of the “secret arts and mysteries of ancient freemasonry,” and included elaborately violent penalties for doing so.[105] Prior to 1990, the temple endowment reportedly also included penalties.[106]
Related Question
Did Joseph Smith teach blood atonement?
Read more in Blood Atonement and Capital Punishment
Why would Joseph have incorporated elements from Freemasonry into the temple endowment?
It's unclear. Joseph rarely discussed how he received revelations.[107] Some historians have suggested that questions and practical problems prompted further revelation or an openness to truth from many places.[108][109]
Some of those around Joseph noted that the prophet believed Freemasonry preserved some things "from the beginning” that he wanted to understand.[110][111]
Why would God use Freemasonry to inspire some aspects of the temple endowment?
The similarities the temple endowment has with Freemasonry may indicate that God used familiar symbols and practices as an accessible framework to reveal eternal truths to Joseph.[112][113]
The Church teaches that the temple endowment is a sacred ceremony designed to teach the plan of salvation and provide a means for individuals to make covenants with God.[114]
Were early Latter-day Saints concerned about the relationship between Masonic rites and the endowment?
No, not really. Early Saints mainly viewed Masonic rites as corrupted forms of the restored temple ceremonies.[115] They also viewed the temple endowment as revelatory and sacred.[116]
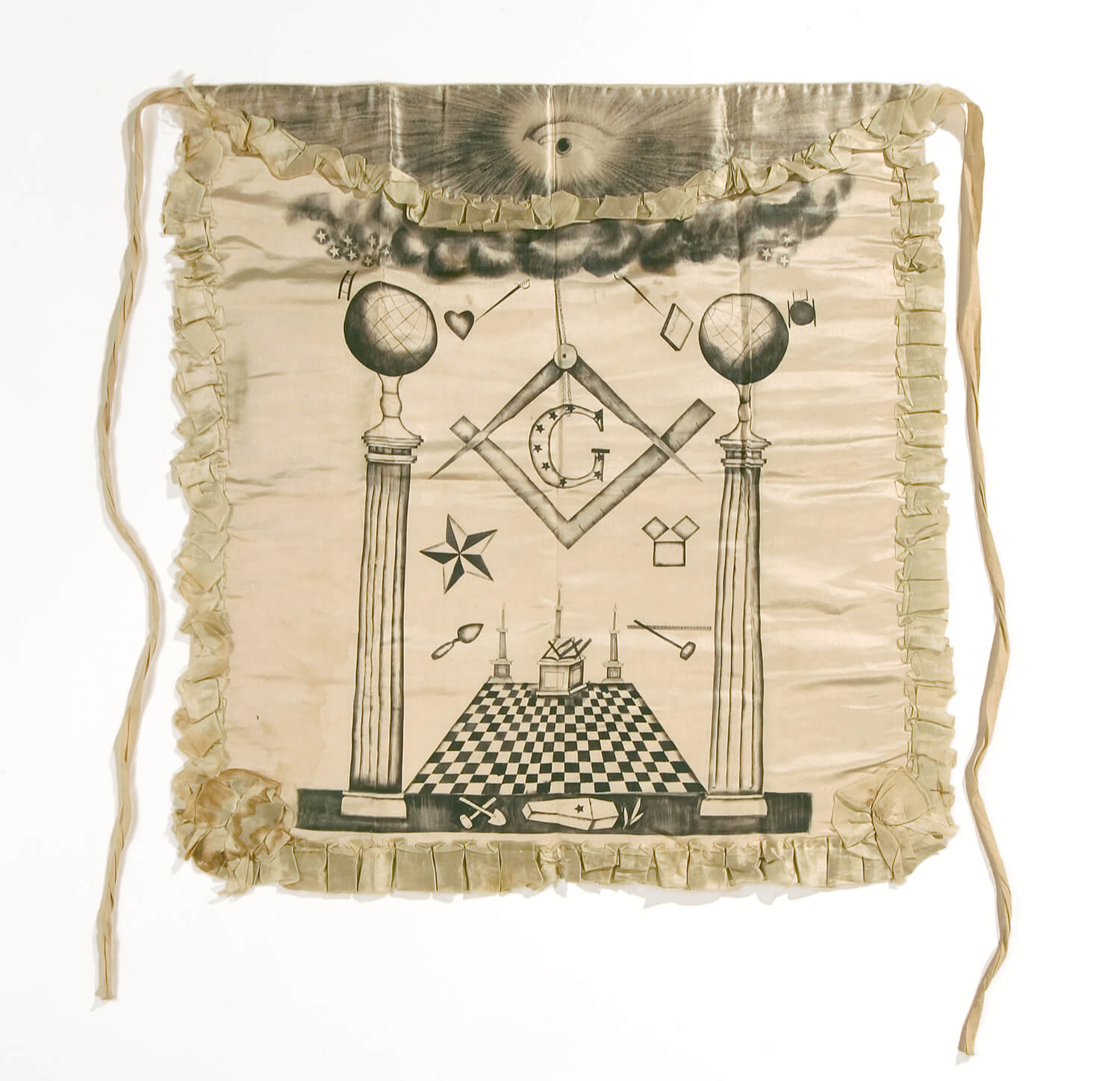

Do Masonic rites and temple ordinances pull from the same sources?
Sometimes. One shared source is the Bible, where both Masonic rites and the temple endowment pull themes and quotes.[118] Some symbols used in both Freemasonry and the endowment, such as the square and compass, can also be found in ancient sources.[119]
Shared Biblical Elements in the Latter-day Saint Temple Endowment and Freemasonry
Element | Bible | Temple Endowment | Freemasonry Rituals |
Bible Stories | Some Biblical stories from the Old Testament (like the creation, the Garden of Eden, and the construction of the tabernacle and Solomon's temple) are also found in the endowment and/or Masonic rituals.[120] | The endowment ceremony incorporates Biblical stories, including the creation and the story of Adam and Eve.[121] | Masonic rituals also draw on biblical narratives, particularly the story of Solomon's Temple and the legend of Hiram Abiff.[122] |
Covenants | The Bible describes several covenants, such as those made with Abraham, Moses, and the Israelites. These covenants are often marked by specific rituals.[123] | In temple ceremonies, Latter-day Saints make sacred covenants with God, including promises of obedience, sacrifice, and consecration.[124] | Freemasons take obligations as part of their initiation that can include moral commitments and promises to support the brotherhood.[125] |
Sacred Clothing | The Bible sometimes speaks of sacred clothing, such as the priestly garments described in Exodus 28.[126] | During the endowment ceremony, members wear sacred temple garments and robes.[127] | Masonic aprons symbolize purity and are worn as part of ritual attire.[128] |
Rituals | The Bible describes rituals such as sacrifices, washings, and anointings, particularly in the context of temple worship in ancient Israel.[129] | The endowment ceremony includes rituals such as washing and anointing, symbolic gestures, and progressive instruction.[130] | Masonic rituals include symbolic gestures, ceremonial instructions, and progressive degrees that teach moral and philosophical lessons.[131] |
Did the practice of Masonry in Nauvoo stop once temple ordinances were introduced?
No. The Saints continued practicing Masonry in Nauvoo until they left in 1846.[132][133]
Related Question
Has the temple endowment changed since its introduction?
Read more in Changes to the Temple Endowment
Did Freemasonry continue among the Saints in Utah?
Not really. The Saints did not establish a Masonic lodge upon arriving in Utah, but groups of non-members eventually did.[134] From 1925 to 1984, the Grand Lodge of Utah prohibited Latter-day Saints from joining Freemasonry within the state.[135]
Freemasonry in Utah
1858
The first Masonic Lodge is established in Utah by non-Latter-day Saint men from Johnston's Army.[137]
August 19, 1860
July 7, 1861
First Presidency counselor Heber C. Kimball emphasizes his loyalty to his country, his Masonic brethren, and the Church.[140]
August 29, 1901
March 11, 1921
1924
January 21, 1925
The Grand Lodge of Utah votes to prohibit Church members from becoming Masons in Utah.[144]
1934
1947
June 4, 1977
1984
The Grand Lodge of Utah changes their policy to admit Latter-day Saints.[148]
February 17, 1992
Church spokesman Don Lefevre states that there is no specific prohibition of Masonry, but that the Church discourages its members from joining it.[149]
2008
2019
The Church posts a video titled "Joseph Smith and Masonry," stating that members are not prohibited from becoming Freemasons.[152]
Have modern Church leaders made any statements about Freemasonry?
No, not directly. Over the years, the Church has made a few statements advising to avoid organizations that are “secret, oath-bound, or [that] would cause [individuals] to lose interest in church activities.”[153] However, a 2019 Church-produced video specifically noted that members are not prohibited from becoming Masons.[154]
- Bill
“There is a podcast called The Ancient Tradition by Jack Logan that explores the similarities and common themes found in ancient religions. There are many fascinating connections between those ancient religions and the temple ceremony and symbols. More interesting than Masons.” - Laurel L. P.
“This was enlightening to me. As a life-long member, I've learned that all history, LDS or not, is messy, and we only know the past as a foreign place because we are only able to look at it through the limited sources available to us.” - Lennarius
“As a Master Mason in good standing and an active, temple recommend-holding member of the Lord’s church, I think this article is fair. One thing I would like to highlight is that freemasonry is de-centralized, and not a unified, worldwide organization. Joseph was a prophet.” - Chris T.
“I’m curious whether you found any information regarding whether or not members are permitted to become Templars in York rite free masonry which specifically requires being Christian. Do the masons consider us Christians?”


 about this topic
about this topic